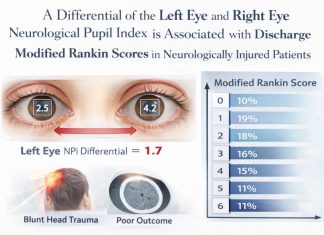
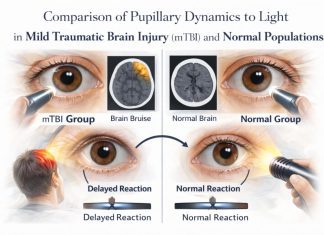
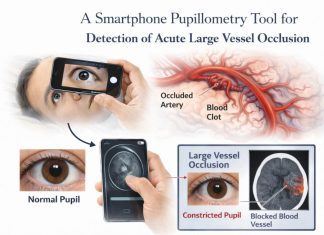
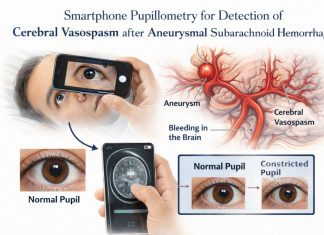
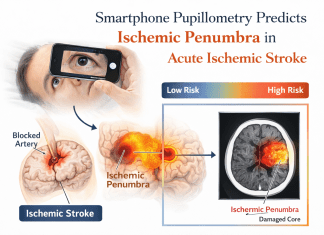
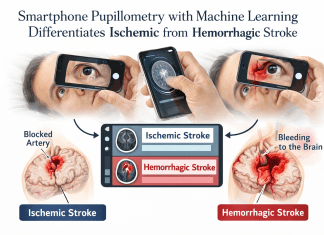
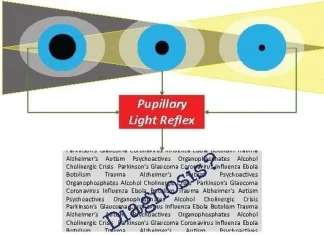
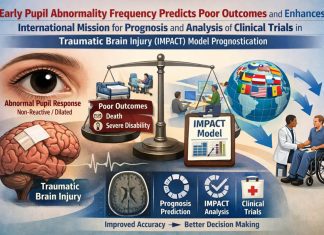
Mission Statement
The Clinical Neuro-Optic Research Initiative (CNRI) advances the science of pupil-based neurodiagnostics by preserving historic clinical insights, developing modern analytic tools, and conducting rigorous research that explores the relationship between ocular micro-structures and systemic health. Our mission is to validate and expand neuro-optic biomarkers that can support future breakthroughs in early detection, monitoring, and non-invasive assessment of autonomic and neurological function.